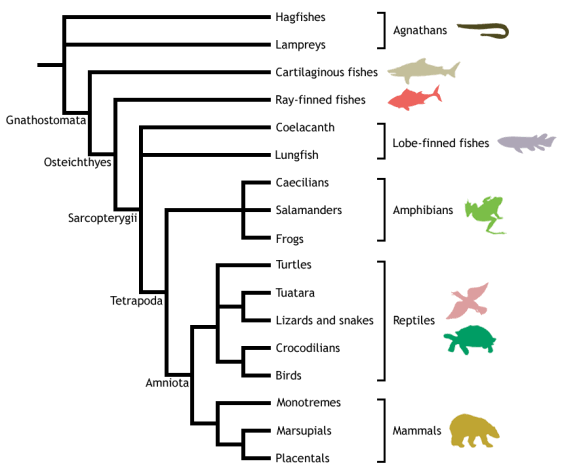
In phylogenetic taxonomy, the relationships between animals are not typically divided into ranks, but illustrated as a nested "family tree" known as a cladogram. Phylogenetic groups are given definitions based on their relationship to one another, rather than purely on physical traits, such as the presence of a backbone. This nesting pattern is often combined with traditional taxonomy in a practice known as evolutionary taxonomy. The cladogram presented below is an example of this pattern.
Traditional taxonomy has living vertebrates grouped into seven classes based on traditional interpretations of gross anatomical and physiological traits. This classification is the one most commonly encountered in school textbooks, overviews, non-specialist, and popular works. The extant vertebrates are: